Tree Topology
Tree Topology
Tree topology can be derived from the star topology. Tree has a hierarchy of various bubs, like you have branches in a tree; hence the name. Figure 1.6 in this case every node is connected to some hub. However, only a few nodes are connected directly to the central hub.
The central hub contains a repeater, which looks at the incoming bits and regenerates them afresh as the full blown signals for 0 or 1 as required. This allows the digital signals to traverse over longer distances. Therefore, the central hub is also called active hubs. The tree topology also contains many secondary hubs, which may be active hubs or passive hubs. The merits and demerits of tree topology are almost similar to those of the star topology.
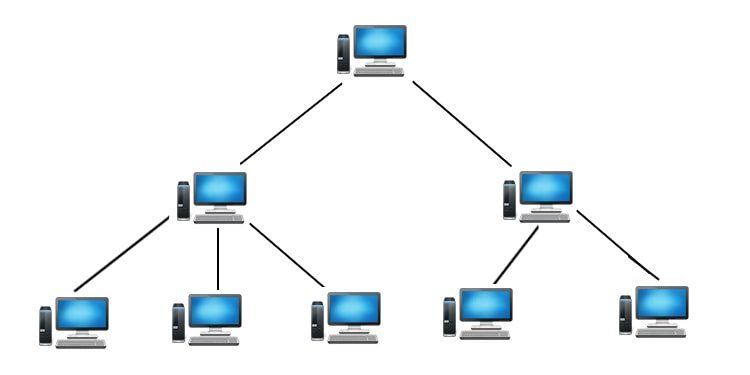
Tree Topology
Advantages of Tree Topology
1. It is an extension of Star and bus Topologies, so in networks where these topologies can't be implemented individually for reasons related to scalability, tree topology is the best alternative.
2. Expansion of Network is possible and easy.
3. Here, we divide the whole network into segments (star networks), which can be easily managed and maintained.
4. Error detection and correction is easy.
5. Each segment is provided with dedicated point-to-point wiring to the central hub.
6. If one segment is damaged, other segments are not affected.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology
1. Because of its basic structure, tree topology, relies heavily on the main bus cable, if it breaks whole network is crippled.
2. As more and more nodes and segments are added, the maintenance becomes difficult.
3. Scalability of the network depends on the type of cable used.
