Analog Transmission
Analog Transmission
Analogue data transmission consists of sending information over a physical transmission medium in the form of a wave. In an analog transmission system, signals propagate through the medium as continuously varying electromagnetic waves. Data is transmitted via a carrier wave, a simple wave whose only purpose is to transport data by modification of one of its characteristics (amplitude, frequency or phase), and for this reason analogue transmission is generally called carrier wave modulation transmission.
Amplitude Modulation
In this modulation, the amplitude of the carrier signal is modified to reflect the analog data
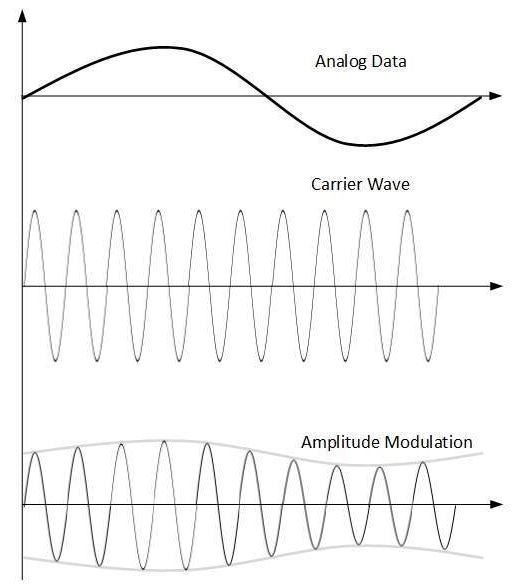
Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude modulation is implemented by means of a multiplier. The amplitude of modulating signal (analog data) is multiplied by the amplitude of carrier frequency, which then reflects analog data.
The frequency and phase of carrier signal remain unchanged.
Frequency Modulation
In this modulation technique, the frequency of the carrier signal is modified to reflect the change in the voltage levels of the modulating signal (analog data)

Frequency Modulation
The amplitude and phase of the carrier signal are not altered.
Phase Modulation
In the modulation technique, the phase of carrier signal is modulated in order to reflect the change in voltage (amplitude) of analog data signal.
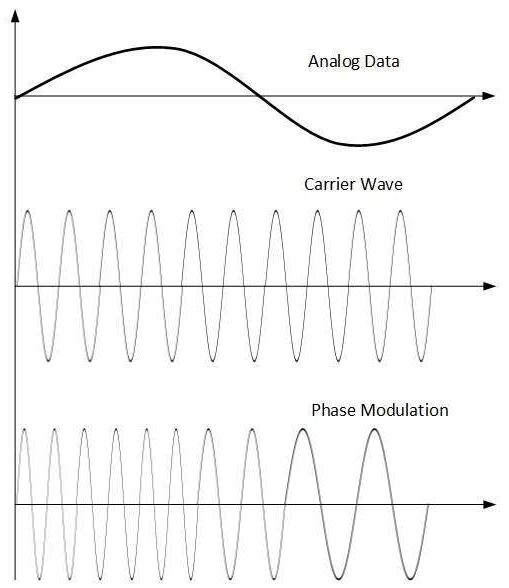
Frequency Modulation
Phase modulation is practically similar to Frequency Modulation, but in Phase modulation frequency of the carrier signal is not increased. Frequency of carrier is signal is changed (made dense and sparse) to reflect voltage change in the amplitude of modulating signal.
