Transmission Media
Transmission Media
Transmission media is a pathway that carries the information from sender to receiver. We use different types of cables or waves to transmit data. Data is transmitted normally through electrical or electromagnetic signals. An electrical signal is in the form of current. An electromagnetic signal is series of electromagnetic energy pulses at various frequencies. These signals can be transmitted through copper wires, optical fibers, atmosphere, water and vacuum Different Medias have different properties like bandwidth, delay, cost and ease of installation and maintenance. Transmission media is also called Communication channel.
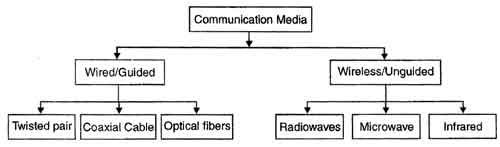
On the basis of transmission of data, the transmission media can be classified in to two categories:
1. Guided (Physical) transmission media
2. Unguided (Wireless) transmission media
Types of Transmission Media
Guided Transmission Media
Wired or Guided Media or Bound Transmission Media: Bound transmission media are the cables that are tangible or have physical existence and are limited by the physical geography. Popular bound transmission media in use are twisted pair cable, co-axial cable and fiber optical cable. Each of them has its own characteristics like transmission speed, effect of noise, physical appearance, cost etc.
The three Guided (Physical) media commonly used for data transmission are:
1. Twisted Pair
2. Coaxial
3. Fiber Optics
Unguided (Wireless) transmission media
Unguided media transport electromagnetic waves without using a physical conductor. This type of communication is often referred to as wireless communication.
1. Radio Transmission
2. Microwave Transmission
3. Infrared
4. Light wave Transmission
