Unguided Media (Wireless Communication)
Unguided Media (Wireless Communication)
Unguided media, also called as wireless communication, transport electromagnetic waves without using a physical conductor. The signals propagate through air (or sometimes water). The communication band for unguided media. We shall concentrate on the radio communications.
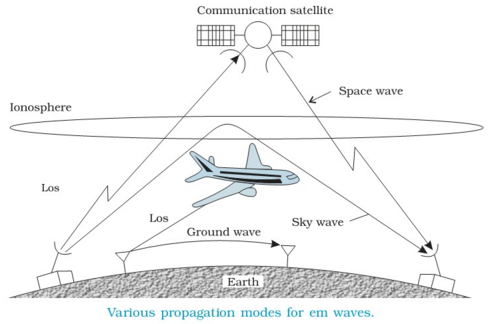
Wireless signals travel or propagated in three ways:
1. Ground-wave propagation
2. Sky-wave propagation
3. Line-of-sight propagation
Ground-wave propagation
Ground Wave Propagation follows the curvature of the Earth. Ground Waves have carrier frequencies up to 2MHz. AM radio is an example of Ground Wave Propagation.
Sky-wave propagation
Ionospheric Propagation bounces off of the Earths Ionospheric Layer in the upper atmosphere. It is sometimes called Double Hop Propagation. It operates in the frequency range of 30 - 85MHz. Because it depends on the Earth's ionosphere, it changes with weather and time of day. The signal bounces off of the ionosphere and back to earth. Ham radios operate in this range. Characteristics of Sky Propagation are as follows: Signal reflected from ionized layer of atmosphere back down to earth; Signal can travel a number of hops, back and forth between ionosphere and earth’s surface; Reflection effect caused by refraction.
Line-of-sight propagation
Line of Sight Propagation transmits exactly in the line of sight. The receive station must be in the view of the transmit station. It is sometimes called Space Waves or Tropospheric Propagation. It is limited by the curvature of the Earth for ground based stations (100 km: horizon to horizon). Reflected waves can cause problems. Examples of Line of Sight Propagation are: FM Radio, Microwave and Satellite. Transmitting and receiving antennas must be within line of sight.