Central Processing Unit
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Central Processing Unit (CPU) or the processor is also often called the brain of computer. CPU consists of Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and Control Unit (CU). In addition, CPU also has a set of registers which are temporary storage areas for holding data, and instructions. ALU performs the arithmetic and logic operations on the data that is made available to it. CU is responsible for organizing the processing of data and instructions. CU controls and coordinates the activity of the other units of computer. CPU uses the registers to store the data, instructions during processing.
CPU executes the stored program instructions, i.e. instructions and data are stored in memory before execution. For processing, CPU gets data and instructions from the memory. It interprets the program instructions and performs the arithmetic and logic operations required for the processing of data. Then, it sends the processed data or result to the memory. CPU also acts as an administrator and is responsible for supervising operations of other parts of the computer.
The CPU is fabricated as a single Integrated Circuit (IC) chip, and is also known as the microprocessor. The microprocessor is plugged into the motherboard of the computer (Motherboard is a circuit board that has electronic circuit etched on it and connects the microprocessor with the other hardware components).
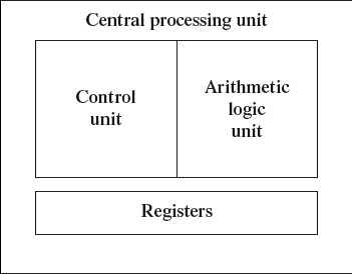
Central Processing Unit
