Web Browser
Web Browser
• Web Browser (or browser) is a software program that extracts information on user request from the Internet and presents it as a web page to the user. It is also referred to as the user interface of the web. Some of the popular web browsers are—Internet Explorer from Microsoft, Mosaic browser, Google’s chrome, and Netscape Navigator from Netscape Inc.
• Browsers are of two types—graphical browser and text-based browser.
• Graphical browsers provide a graphical user interface where the user can jump from one web page to the other by clicking on the hyperlink (displayed in blue color with underline) on a web page. Internet Explorer, Chrome and Mosaic are examples of graphical browsers.
• Text browsers are used on computers that do not support graphics. Lynx is a text browser.
• The process of using browser to view information on the Internet is known as Browsing or Surfing. During browsing, the user can navigate from one web page to another using URLs, hyperlinks, browser navigation tools like forward and back button, bookmarks etc.
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
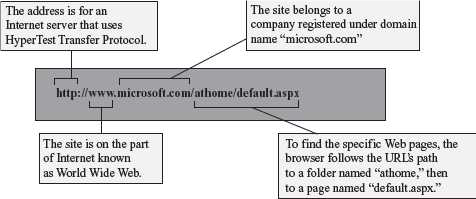
A web page on the Internet is uniquely identified by its address, called URL. URL is the address on the Internet at which the web page resides. The user uses this address to get a web page from the Internet. The general form of URL is :
protocol://address/path
where,
• protocol defines the method used to access the web page, e.g., http, ftp, news etc.
• address is the Internet address of the server where the web page resides. It contains the service (e.g. www) and the domain name (e.g. google.com)
• path is the location of web page on the server.
To access documents on WWW, the HTTP protocol is used. An example of a URL is,
http://www.dsc.com/mainpage
http is the protocol, www.dsc.com is the address, and mainpage is the path.